Watch our series of short interviews about ICCWC impact in West and Central Africa.
- Assane Drame - Regional Coordinator for West and Central Africa, UNODC
- Birame Sidi Kane - Director of the WCO Regional Liaison Office, Senegal
- Grace Ngakala - Deputy Public Prosecutor, Republic of Congo
- Mamadou Dian Boro DIALLO - Attorney General, Republic of Guinea
- Salimata Kone - Director of Wildlife and Energy Resources, Côte d'Ivoire
With ICCWC support, UNODC in partnership with TRACE Wildlife Forensics Network, set up a forensics wildlife laboratory in Uganda. The lab supports wildlife crime investigations and prosecutions in Uganda and other African countries.
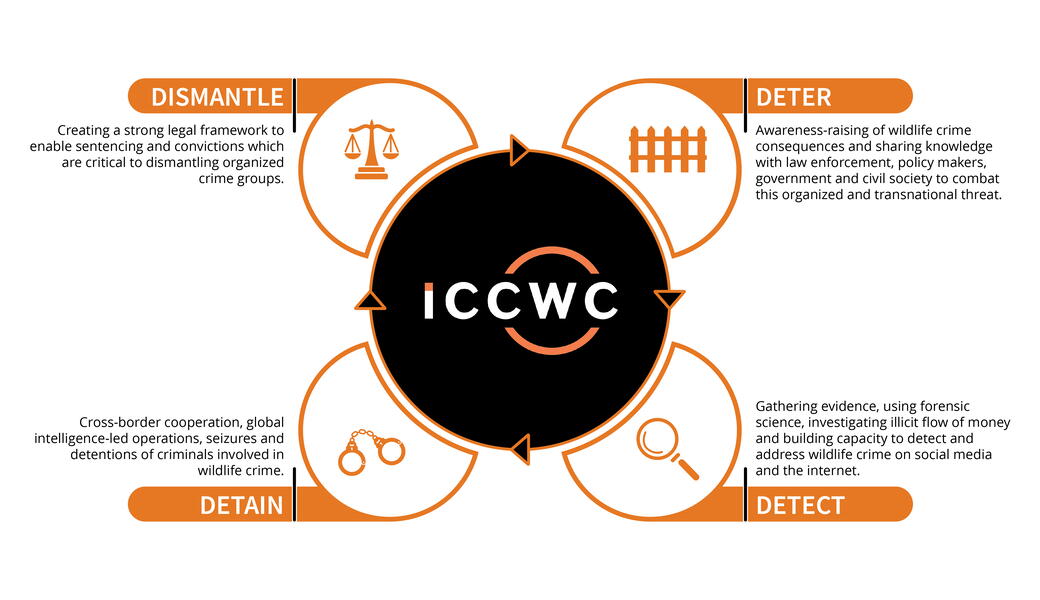
The ICCWC Menu of Services provides an indicative list of the training courses, tools and services available through ICCWC partner agencies. Delivery, mobilization and implementation of these are subject to availability of resources and identified priorities. The menu of services is structured against seven headings in accordance with the type of activity that can be delivered or supported, noting that some interventions are cross cutting and may happen at various stages. The activities listed in this menu of services are not exhaustive. They present examples of what could be implemented by ICCWC in different countries or regions upon request and in collaboration with relevant national authorities or regional bodies and networks. Other tailored activities and interventions can also be developed based on specific needs identified and requirements of countries and regions.

The ICCWC Wildlife and Forest Crime Analytic Toolkit provides government officials, Customs, police and other relevant enforcement agencies with a framework to conduct a comprehensive analysis of their response to wildlife and forest crime and identify their technical assistance needs. The countries capabilities are assessed in relation to relevant legislation, law enforcement measures, prosecutorial and judicial capacities, factors that drive offences, the effectiveness of preventive measures, and the availability and use made of data. The Toolkit is designed to serve as a framework around which a prevention and response strategy can be developed.
An overview of the implementation of the ICCWC Toolkit can be found here
For further details, please see the ICCWC Toolkit Fact Sheet and the Toolkit implementation step by step guide.
Read the brochure available in Chinese (Mandarin), English, French, Russian and Spanish.

The ICCWC Indicator Framework for Combating Wildlife and Forest Crime is a tool to enable countries to measure and monitor the effectiveness of their law enforcement responses to wildlife and forest crime. It has been developed to complement the ICCWC Toolkit and provides a standardized framework to monitor any changes in national law enforcement capacity and effectiveness over time. The ICCWC Indicator Framework is a comprehensive set of 50 indicators arranged against eight desired outcomes of effective law enforcement to combat wildlife crime. Designed as a self-assessment tool it is best completed through a collaborative process involving all relevant national law enforcement agencies.
An overview of the implementation of the ICCWC Indicator Framework can be found here.
Step by step guidelines are available in Chinese (Mandarin), English, French, Russian and Spanish.
Read the brochure available in Chinese (Mandarin), English, French, Russian and Spanish.

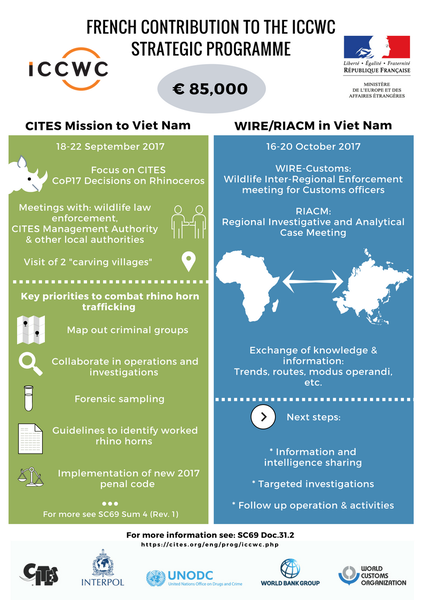
The Guidelines on methods and procedures for ivory sampling and laboratory analysis support the deployment of forensic technology to combat elephant poaching and the associated illegal trade in ivory. It has been developed by ICCWC together with experts from around the world. The Guidelines are aimed at first responders, investigators, law enforcement officials, forensic scientists, prosecutors and the judiciary. Their purpose is to facilitate the use of forensic science to the fullest extent possible in order to combat wildlife crime, and in particular, to combat the trade in illegal ivory through the provision of guidance to support transnational criminal investigations and law enforcement operations.
To complement the Guidelines, ICCWC has also developed a training video on ivory sampling that is available in Arabic, Chinese, English and French.
Read the brochure available in Chinese (Mandarin), English, French, Russian and Spanish.

The Best Practice Guide for Forensic Timber Identification Guide cover the whole chain of custody, providing information on best practices and procedures from the crime scene to the court room, in order to ensure that forensic data are credible and admissible in court. Its purpose is to facilitate more timely, thorough and effective investigations, resulting in an increased number of successful prosecutions and a reduction in the illegal timber trade. In addition, ICCWC has developed a complementary 'Law Enforcement Best Practice Flow Diagram for Timber' to lead front-line officers through the steps that should be completed when dealing with a load or shipment containing timber. The Guidelines are available in English and Spanish.
An online version of this Flow Diagram is available in English, together with further dynamic links to additional resources.
Read the brochure available in Chinese (Mandarin), English, French, Russian and Spanish.

A number of networks with different purposes and objectives focused on combating wildlife crime, and with varying degrees of formality and organization, have been developed across the world. In most cases these networks are known as Wildlife Enforcement Networks (WENs). These WENs if functioning optimally, can play an important role in facilitating increased collaboration and coordination to combat wildlife crime. The ICCWC Guidelines for Wildlife Enforcement Networks (WENs) outline the key considerations in the development of a new WEN, and also provide a self-assessment tool for use by existing WENs to assist them in evaluating their level of maturity and/or operational performance and identify areas that could be further strengthened.
Read the brochure available in Chinese (Mandarin), English, French and Spanish.

-
The CITES Virtual College provides capacity-building activities and reference materials online.
-
A directory of laboratories conducting wildlife forensic testing, able and willing to carry out wildlife forensics analyses upon request from other countries and meeting specific criteria, is available on the CITES Wildlife forensics webpage.
-
CITES Enforcement Authority Forum has been integrated with ENVIRONET. For details, see Notification 2015/039.
-
Capacity established by INTERPOL is available to Parties through the INTERPOL General Secretariat (IPSG) in Lyon, France. For advice and assistance to combat wildlife crime linked to the Internet. For details, see Notification 2020/031.
-
To view the full list of trainings, please see the ICCWC Menu of Services.
-
WCO CLiKC! CITES E-learning modules for Customs Officials available on
Coordination among donors is important to ensure aligned and effective support to countries affected by illegal wildlife trade (IWT).
The objective of this guidance note is to share experiences and case studies on strengthening national-level donor and development partner coordination to combat IWT. Little information currently exists on what coordination mechanisms are used globally and what has been learned from their operation. This guidance note seeks to close this knowledge gap.

Download
EnglishThe Environmental and Natural Resource Crimes Risk Assessment Module (Module 10) is a voluntary tool developed by the World Bank Group to help countries identify and address their vulnerability to financial crimes in the environmental and natural resource sectors. It can be taken independently or as part of the broader National Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing Risk Assessment Toolkit. Countries are advised to use the NRA Toolkit with technical assistance from the WBG to ensure proper application.

Download
EnglishThe Customs – Police Cooperation Handbook (2018) aims to foster increased cooperation between customs and police agencies at the national level. The Handbook highlights the need for customs – police cooperation, and, offers professional insight on how to strengthen the collaboration between these institutions.

Download
EnglishThe Guide on Drafting Legislation to Combat Wildife Crime (2018) aims is to assist Parties in protecting wildlife by criminalizing serious wildlife offences, thereby enhancing Parties prosecution and criminal justice capacities. The Guide is intended as a technical assistance tool to assist Parties in reviewing and amending existing legislation and adopting new legislation against wildlife crime in line with the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime and the United Nations Convention against Corruption.

Download
EnglishThe Rotten Fish - A Guide on Addressing Corruption in the Fisheries Sector is designed to help policymakers with the challenging task of identifying the specific areas in their legal and regulatory frameworks susceptible to corruption, and to act to address those weaknesses. It also aims to sensitize the authorities working on fisheries management to the threat that corruption poses. And where corruption already has gained a foothold, the guide suggests ways to reduce its impact and develop safeguards to prevent its return.

Download
EnglishThe Scaling Back Corruption - A Guide on Addressing Corruption for Wildlife Management Authorities serves as a reference tool to assist wildlife management authorities, including CITES Management and Scientific Authorities, in developing their capability to tackle the corruption risks that can undermine their work, and by doing so proactively reduce the occurrence, extent and negative impact of wildlife crime.

Download
EnglishThe Wildlife Crime Scene Guide for First Responders was developed as a basic guide to assist and guide those who are first responders to wildlife crime scenes, including those operating under sub-optimal conditions with limited personnel and equipment.

Download
EnglishThe Wildlife Crime Linked to the Internet - Practical Guidelines for Law Enforcement Practitioners was developed to assist Parties in combating wildlife crime linked to the Internet more effectively.
The guidelines which includes matters such as concepts related to the technology used for online investigations, how to identify wildlife crime linked to the Internet, disrupting wildlife crime linked to the Internet, analyzing content and modern police investigation techniques, provides a practical tool for law enforcement officers on how to investigate cases of wildlife crime linked to the Internet.
The full version of the guidelines is restricted to law enforcment authorities only. The document is available in Arabic, English, French and Spanish upon request to INTERPOL (environmentalcrime [at] interpol.int (environmentalcrime[at]interpol[dot]int)) via each country’s respective National Central Bureau.

Download
EnglishThe aim of the Customs-FIU Cooperation Handbook is to serve as a practical tool for Financial Intelligence Units (FIUs) and Customs Services as well as other law enforcement authorities (such as certain National Police Services) with competences in cross-border related investigations. The Handbook serves as an orienting guide for these authorities and addresses mechanisms and institutionalized practices whereby the Customs Services and FIUs can most effectively collaborate in targeting and dismantling transnational organized crime engaged in international money laundering and terrorism financing activities.

Download
EnglishThe World Wildlife Crime reports produced by UNODC in cooperation with ICCWC partners’ takes stock of the wildlife crime situation with a focus on illicit trafficking of specific species of wild fauna and flora. It provides a broad assessment of the nature and extent of the problem at the global level. The reports include quantitative market assessments and a series of in-depth illicit trade case studies for species increasingly being seized by authorities as they gain prominence among consumers.

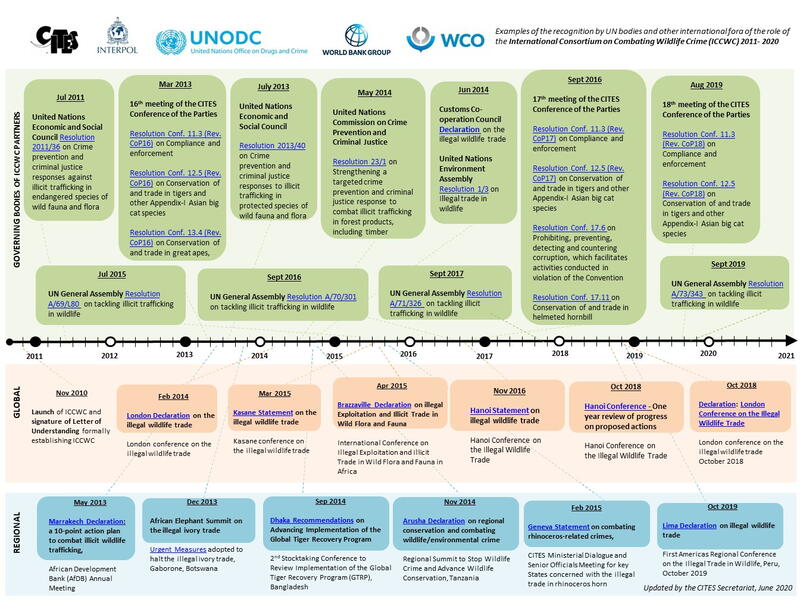
For 15 years, the International Consortium on Combating Wildlife Crime (ICCWC) has been working with and supporting Parties to take stronger, smarter, and more coordinated action against wildlife and forest crime.
To mark ICCWC’s 15-year milestone, this publication takes the reader across 15 achievements over the 15 years. It shows how countries have strengthened their ability to detect, investigate, prosecute, and deter wildlife crime with ICCWC support, protecting biodiversity and people around the world and bringing those responsible for wildlife crime to justice.

Download
EnglishICCWC has established a long-term vision of a world free of wildlife crime. The ICCWC Vision 2030 outlines how ICCWC will work towards a world free of wildlife crime by 2030, following a Theory of Change designed to support and strengthen wildlife authorities, police, customs and criminal justice systems to ensure that they effectively respond to the threat.

Access the official documents from the CITES Standing Committee, responsible for overseeing the implementation of CITES decisions between Conferences of the Parties. These documents include reports, recommendations, and policy updates, guiding the ongoing efforts to regulate wildlife trade and protect endangered species worldwide.
Explore the official documents from the CITES Conference of the Parties (CoP), where global representatives convene to discuss and make decisions on wildlife trade regulations. These documents include meeting agendas, resolutions, and proposals aimed at protecting endangered species and ensuring sustainable trade.


Related content
Our focus: Wildlife and Forest Crime
What is wildlife and forest crime? ICCWC considers ‘wildlife’ to include all wild fauna and flora, including animals, birds and fish, as well as timber and non-timber forest products. ‘Wildlife crime’ refers to the illegal taking, trading (supplying, selling or trafficking), importing, exporting, processing, possessing, obtaining and consumption of wild...
4th Global Meeting of Wildlife Enforcement Networks
4th Global Meeting of Wildlife Enforcement Networks The Secretariat of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), in cooperation with its partners from the International Consortium on Combating Wildlife Crime (ICCWC) and with generous funding support from the United States of America convened...
Wildlife Enforcement Networks (WENs)
What are Wildlife Enforcement Networks? Regional and inter-regional cooperation is essential to combating wildlife trafficking effectively. A number of networks with different purposes and objectives focused on combating wildlife crime, and with varying degrees of formality and organization, have been developed across the world. In most cases these networks are...